- Interest-rate Risk and Household Portfolios [pdf]
with Max Miller, James Paron and Natasha Sarin
Reject & Resubmit at the American Economic Review
How are households exposed to interest-rate risk? When rates fall, households face lower future expected returns but those holding long-term assets—disproportionately the wealthy and middle-aged—experience capital gains. We study the hedging demand for long-term assets in a portfolio choice model. The optimal interest-rate sensitivity of wealth is hump-shaped over the life cycle. Within cohorts, it increases with wealth and earnings. These predictions fit observed patterns in the United States, suggesting a relatively efficient distribution of interest-rate risk. By protecting workers from rate fluctuations, Social Security limits the welfare consequences of rising wealth inequality when rates fall.
- Robustness Checks in Structural Analysis [pdf]
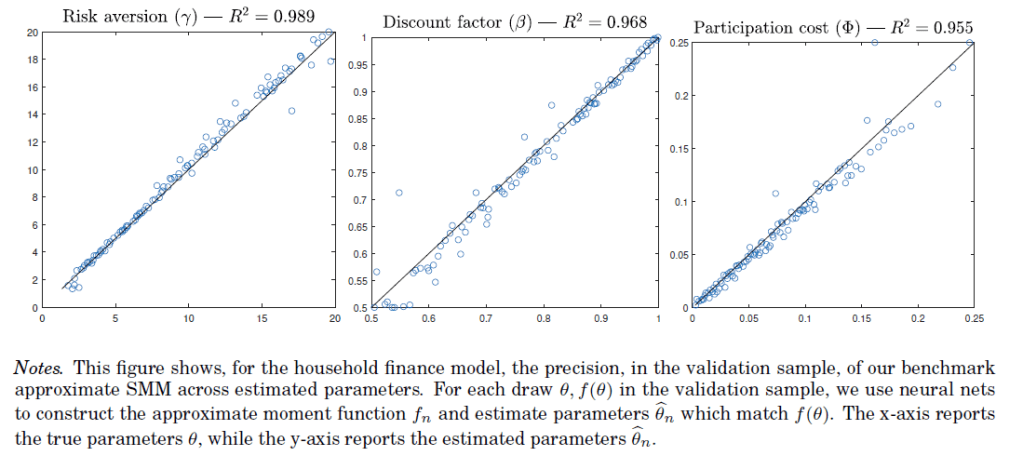
with Mehran Ebrahimian, Mohammad Fereydounian, David Sraer and David Thesmar
This paper introduces a computationally efficient methodology for estimating variants of structural models. Our approach approximates the relationship between moments and parameters, offering a low-cost alternative to traditional estimation methods. We establish general convergence conditions, primarily requiring model-based moments to be continuous functions of parameters. While this continuity does not necessitate a continuous economic model, it does require the model to have only sparse discontinuities, a concept we define. We also provide convergence rate bounds for Kernel and Neural Net approximations, with the latter demonstrating superior performance in higher dimensions. We apply this methodology to two standard structural models: (1) dynamic corporate finance and (2) life-cycle portfolio choice. We demonstrate the reliability of our approach through simulations and then use it to explore identification, robustness to sample splits and moment selection, and model misspecification. These explorations are computationally infeasible with standard techniques, but become trivial with our methodology.
Performance of SMM Approximation using neural nets — household finance model
- Labor Market Risk and the Private Value of Social Security [pdf]
Social Security provides insurance against idiosyncratic income risk but exposes workers to systematic risk because benefits are indexed to the evolution of aggregate earnings. I calibrate a life-cycle model to compare workers’ certainty equivalent valuation of Social Security to its net present value discounted at the risk-free rate. I show that, overall, labor market risk reduces current workers’ private value of Social Security by 46%. This adjustment sums up to $11.4 trillions on the national scale and the equity premium is its main determinant. For workers under 30, the certainty equivalent of Social Security is negative. Exposure to systematic risk through Social Security peaks relatively late in the life-cycle.